Transcriptional analysis of impacts of glycerol transporter 1 on methanol and glycerol metabolism in Pichia pastoris.
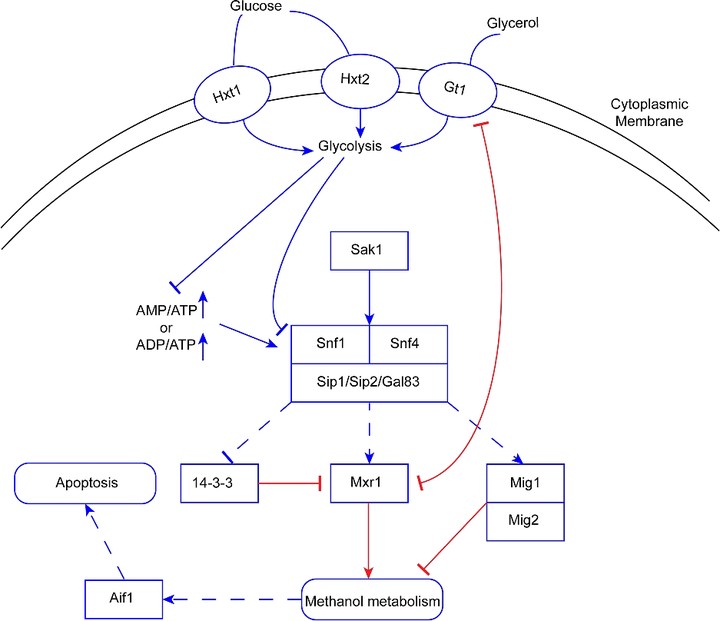 AMPK/SNF1 pathway is likely to promote methanol metabolism.
AMPK/SNF1 pathway is likely to promote methanol metabolism.Abstract
The efficient promoter of alcohol oxidase 1 (PAOX1) in methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris is strictly induced by methanol but repressed by glycerol with an unclear molecular mechanism. In the present study, the gene of a previously characterized transmembrane protein glycerol transporter 1 (GT1) of P. pastoris GS115 was deleted by homologous recombination. Transcriptional profiles of the mutant (gt1Δ) and wild type (WT) were compared with different carbon sources (glycerol, methanol and glycerol-methanol mix) at various time points using high-throughput RNA-Seq techniques. We determined that the loss of glycerol transporter 1 (Gt1p) could relieve catabolite repression in the glycerol-methanol mixed medium and shared a similar transcriptional profile with the WT in methanol medium. By calculating the common differentially expressed genes in three distinct paired groups, genes involved in the stress response, nutrition deprivation and translational process were identified, explaining the potential roles of glycerol in the regulation of methanol metabolism. Based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis, the relationship between biological traits and the transcriptional profile was established. With the support of published research and our data, we propose two possible regulatory pathways that are involved in the regulation of catabolite repression (adenosine 5΄-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase /SNF1 and Mitogen-activated protein kinase/HOG), thereby providing potential targets for both research and industrial strain improvement.